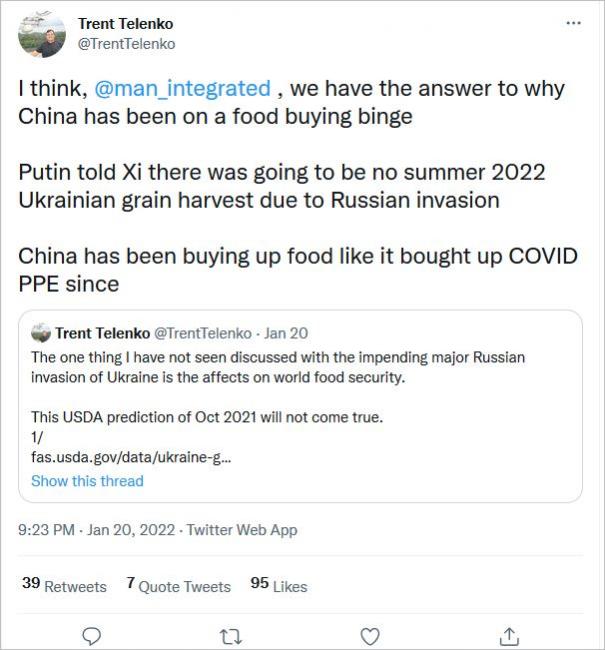
Bloomberg and other media reporting China massively stockpiling food essential, War fears muted
ByAdam Minter5 January 2022, 01:00 GMT
In recent months, food prices have hit 10-year highs, causing concern worldwide. Supply-chain bottlenecks, labor shortages, bad weather and a surge in consumer demand are among the factors responsible for the spike. So, too, is a lesser-known phenomenon: China is hoarding key commodities.
By mid-2022, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, China will hold 69% of the world’s corn reserves, 60% of its rice and 51% of its wheat. By China’s own estimation, these reserves are at a “historically high level” and are contributing to higher global food prices. For China, such stockpiles are necessary to ensure it won’t be at the mercy of major food exporters such as the U.S. But other countries, especially in the developing world, might ask why less than 20% of the world’s population is hoarding so much of its food.
China has operated granaries for thousands of years. In imperial times, they served as a source of tax revenue and a means of managing bad harvests, natural disasters, and war. Their importance grew as China’s population soared, yet the state’s ability to manage them faltered. During the late 19th and early 20th centuries, natural and political disasters brought hunger and starvation to millions. Outsiders referred to China as “the land of famine.” Political instability and revolution soon followed.
Mao Zedong and China’s Communist Party staked much of their credibility on “solving” hunger, but midcentury famines took the lives of tens of millions. President Xi Jinping, never one to criticize his own country, once remarked that many members of his generation still recall hunger. Those memories have informed Xi’s policies since the start of his regime. In 2013, just weeks after taking office, Xi endorsed a nationwide campaign to discourage people from wasting food. In 2020, the “clean-plate campaign” was resurrected as he called on Chinese to “maintain a sense of crisis about food security.”
That crisis isn’t just about having enough to eat. It’s about having enough food produced domestically to minimize reliance on anyone else. Two weeks ago, Xi told a high-level Communist Party meeting that “the food of the Chinese people must be made by and remain in the hands of the Chinese people.”
That won’t be easy. China’s inventory of arable land has been in decline for decades, nibbled away by urban development and soil contamination, and its farms are far less productive than counterparts in other countries. Efforts to boost productivity with policy incentives and technology investments are promising but unlikely to pan out for years.
So China is stockpiling. At home, the government is offering farmers a minimum price for their crops (which are then often stockpiled). In March, it raised the minimum price for wheat for the first time since 2014. Meanwhile, traders have taken advantage of a strengthening yuan to snap up grains at a feverish pace. China’s wheat imports surged 50% between January and July, compared to the same period of 2020.
The size and content of China’s commodity stockpiles is a jealously guarded state secret. But officials have been unusually open about the matter lately. In November, after a vaguely worded government missive about potential shortfalls this winter caused nationwide panic, agricultural officials announced that China had enough wheat stockpiled to last 18 months.
Other countries have been building up food reserves too, of course, especially as Covid-related disruptions persist. In June, the UN’s food agency warned that some low-income countries were likely to see food import costs jump as much as 20% for the year. Though the report didn’t single out any country for responsibility, China — as the world’s largest agricultural importer — certainly plays a crucial role.
Right or wrong, China has no intention of unwinding its stockpiles for the benefit of others. Nonetheless, there are steps it could take to help mitigate inflation. Most important, it should begin unwinding crop supports that raise domestic food prices beyond global ones. Meanwhile, a more open acknowledgement of China’s inevitable role in driving food inflation might encourage its leaders to work with others on food assistance to low-income regions.
China’s evolution from famine to feast delivered hundreds of millions of people from hunger. As its economy and clout grows, it should seek to ensure that others can enjoy the bounty.
-
Comments (15)
-